PRE-OPERATIVE ANGIOEMBOLIZATION
What is pre-operative embolization:
- It is a minimally invasive procedure in which tumour embolization done through feeder artery.
Why it is necessary:
- Aim of procedure is reducing risk of bleeding during surgery and making complete excision of tumor feasible (better visualisation of tumor margin during surgery so complete removal possible).
When it should be performed:
- Many of the tumors that occur in the head, neck, and spine have a large and extensive blood supply.
- These tumors include
- Meningiomas (tumors of the covering of the brain)
- Paragangliomas or glomus tumors (tumors associated with nerves of the head and neck),
- Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas (tumors of the nose that occur in young males),
- Tumors of the bones of the spine (vertebral haemangioma or metastasis).
- It is generally performed 24-48 hrs before surgery, by which blood supply of tumor is completely stop or decrease.
How it is performed:
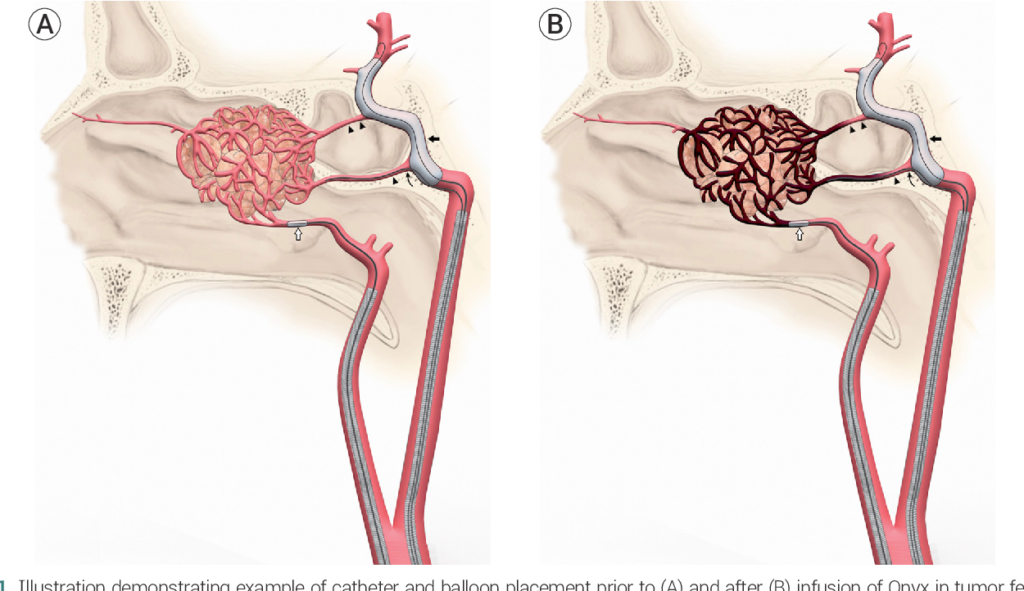
- In angioembolisation, a catheter is placed into arteries supplying the tumor. Material is injected to block off the blood supply to the tumor.
- There are many different kinds of materials available for this, depending on the type of tumor, its location, and the size of the blood vessels.
- Sometimes, especially in the case of tumors of the vertebrae (or other bones), a needle is inserted through the skin directly into the bone containing the tumor and material is injected to block the blood supply or kill the tumor.
Preparation for procedure:
- Few basic blood investigations like CBC, PT/INR, viral markers.
- Bring all the records including imaging record.
- Signing consent form.
What are risks:
- Vary with site of embolization; non-target embolization, infection (<1 case in 1000).