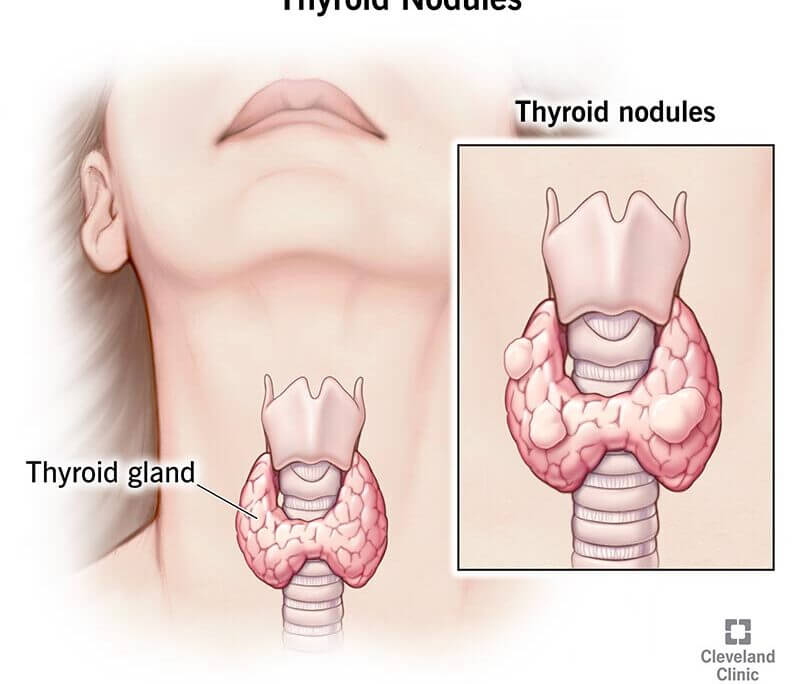
The thyroid gland, located at the base of your neck, plays a crucial role in regulating your metabolism. Sometimes, however, nodules or tumors can develop within the thyroid. These can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Traditionally, surgery and radioactive iodine therapy (RAI) have been the main treatment options for thyroid tumors. However, a newer, minimally invasive technique called thyroid ablation is gaining traction.
This blog post will delve into thyroid ablation, exploring its effectiveness for both solid and cystic thyroid tumors, with a specific focus on the image-guided (IR) method of treatment.
What is Thyroid Ablation?
Thyroid ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses either radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or ethanol ablation to destroy thyroid tissue.
- RFA: This technique employs radio waves to generate heat, which shrinks or destroys the targeted tissue.
- Ethanol ablation: Involves injecting concentrated alcohol directly into the nodule, causing it to shrink and harden.
Both procedures are performed with image guidance, typically ultrasound, to ensure precise targeting of the nodule.
Benefits of Thyroid Ablation
Compared to traditional treatments, thyroid ablation offers several advantages:
- Minimally invasive: No large incisions are required, reducing recovery time and scarring.
- Outpatient procedure: In most cases, you can go home the same day as the ablation.
- Preserves healthy thyroid tissue: Unlike surgery, which removes the entire thyroid gland or a portion of it, ablation only targets the affected area.
- Reduced risk of complications: Less invasive than surgery, leading to fewer potential complications.
Is Thyroid Ablation Right for You?
The suitability of thyroid ablation depends on several factors, including:
- The size and type of your nodule (solid or cystic)
- Whether the nodule is cancerous or benign
- Your overall health
IR-Guided Thyroid Ablation
Image-guided (IR) ablation is the preferred method for thyroid ablation. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Preparation: You’ll likely receive local anesthesia to numb the area around your neck.
- Image Guidance: Using ultrasound or other imaging techniques, the doctor locates the exact position of the nodule.
- Needle Insertion: A thin needle is inserted into the nodule under image guidance.
- Ablation: RFA or ethanol is delivered through the needle to destroy the targeted tissue.
- Monitoring: After the procedure, you’ll be monitored for a short period to ensure there are no complications.
Effectiveness for Solid and Cyctic Tumors
- Solid Tumors: Studies have shown promising results for RFA in treating benign, predominantly solid thyroid nodules. However, for malignant tumors, surgery remains the gold standard treatment.
- Cyctic Tumors: Ethanol ablation is particularly effective for cystic nodules, with significant reduction in size reported in studies.
Important Considerations
- Thyroid ablation is a relatively new procedure, and long-term data is still being collected.
- The procedure may not be suitable for all types of thyroid tumors.
- There’s a possibility of needing repeat ablation for some cases.
Thyroid Ablation: A Minimally Invasive Option for Solid and Cyctic Tumors
In addition to the information covered in the previous section, here’s more detail on thyroid ablation for solid and cystic tumors, including pre-procedural steps and post-procedural care:
Pre-Procedural Steps
- Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: This minimally invasive procedure is crucial for determining whether a nodule is cancerous or benign. A thin needle is used to extract a small sample of tissue from the nodule, which is then examined under a microscope.
- Thyroid Function Tests: These blood tests assess the functionality of your thyroid gland and ensure it’s producing the right amount of hormones.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI scan might be used to evaluate the size, location, and characteristics of the nodule.
- Consultation: Your doctor will discuss the details of the ablation procedure, potential risks and benefits, and answer any questions you may have.
Post-Procedural Care
- Recovery: After the ablation, you’ll be monitored for a short period to ensure there are no complications. Most patients can go home the same day with minimal discomfort.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medication can be used to manage any post-procedural discomfort.
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are essential to monitor the effectiveness of the ablation and your thyroid function. Repeat imaging tests might be needed to track the size of the nodule.
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement: If a significant portion of your thyroid gland is destroyed during ablation, you may need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to maintain optimal hormone levels.
Additional Considerations for Solid Tumors
- Type of Cancer: While ablation might not be the primary treatment for malignant solid tumors, it can be considered for recurrent papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (a very small type of thyroid cancer) after surgery and RAI.
- Multifocality: If you have multiple nodules in the thyroid, ablation might not be the best option, as it may not be able to target all affected areas.
Future of Thyroid Ablation
Research on thyroid ablation is ongoing, and advancements are being made in technology and techniques. Here are some promising areas:
- Improved Targeting: Newer ablation techniques with even more precise targeting could lead to better treatment outcomes.
- Combined Therapies: Combining ablation with other treatments like RAI or medication might offer a more comprehensive approach for specific cases.
- Long-Term Data: As the use of thyroid ablation increases, long-term data on its effectiveness and potential complications will become more robust.
Conclusion
Thyroid ablation offers a promising minimally invasive alternative for treating both solid and cystic thyroid nodules. While it might not be suitable for all cases, it presents a valuable option for select patients. Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is crucial to determine if thyroid ablation is the right course of action for you.