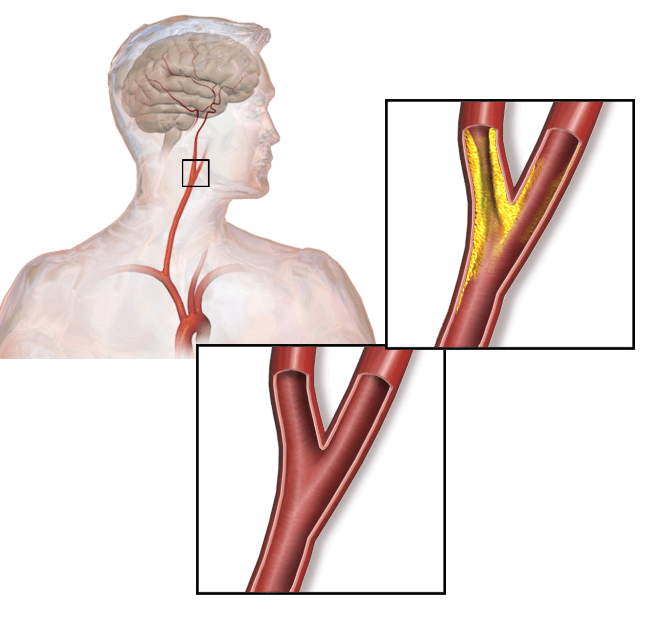
Carotid stenosis, a narrowing of the carotid arteries, can be a ticking time bomb for your brain health. These vital vessels, located on either side of your neck, are responsible for supplying blood rich in oxygen and nutrients to your brain. When plaque, a fatty substance similar to what clogs coronary arteries, builds up in these arteries, it restricts blood flow, significantly increasing your risk of stroke.
While some people with carotid stenosis may not experience any symptoms, others may have warning signs that shouldn’t be ignored. This blog delves deep into understanding carotid stenosis, its potential consequences, the diagnostic tools used to identify it, and the various treatment options available, including a detailed look at the minimally invasive procedure known as carotid artery stenting (CAS) performed by interventional radiologists.
Understanding the Threat: Carotid Stenosis and Stroke Risk
The brain relies on a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients carried by blood to function properly. When the carotid arteries become narrowed due to plaque buildup, this crucial supply gets hampered. Depending on the severity of the stenosis (narrowing), blood flow can be significantly reduced, leading to:
- Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs): These are temporary episodes with stroke-like symptoms that usually resolve within minutes or hours. They serve as a warning sign of a potential stroke in the future.
- Stroke: A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is completely blocked, causing brain tissue damage. Strokes can lead to lasting neurological impairments like paralysis, speech difficulties, and cognitive decline.
- Other Neurological Issues: Depending on the location and severity of the stenosis, some individuals may experience dizziness, weakness, or numbness on one side of the body, or difficulty speaking.
Recognizing the Warning Signs: When to Seek Medical Help
Early detection and treatment of carotid stenosis are crucial to prevent a stroke. While some people with this condition may not experience any symptoms, others may exhibit red flags that warrant immediate medical attention. Here are some signs to watch out for:
- Sudden onset of weakness or numbness on one side of the face, arm, or leg.
- Difficulty speaking or slurred speech.
- Sudden vision problems in one or both eyes.
- Severe dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Transient episodes of weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking that resolve within minutes or hours (TIAs).
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly reduce your risk of stroke and its devastating consequences.
Diagnosing Carotid Stenosis: Unveiling the Blockage
Fortunately, there are several painless and effective diagnostic tools available to identify carotid stenosis and determine the severity of the blockage. These include:
- Ultrasound Doppler: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to assess blood flow through the carotid arteries. It can detect blockages and measure the degree of narrowing.
- Angiography (CTA/MRA): These imaging techniques use X-rays or magnetic fields to create detailed pictures of the carotid arteries. CTA (computed tomography angiography) employs X-rays and a contrast dye to visualize the arteries, while MRA (magnetic resonance angiography) uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images. Both techniques can pinpoint the location and extent of the blockage.
Treatment Options for Carotid Stenosis: Tailoring the Approach
The treatment approach for carotid stenosis depends on various factors, including the severity of the blockage, your overall health, and your risk of stroke. Here’s a breakdown of the available options:
- Lifestyle Modifications: As with many health conditions, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve your cardiovascular health and reduce your risk of stroke. This includes maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing cholesterol and blood pressure through medication if necessary.
- Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA): This surgical procedure involves removing plaque buildup from the carotid artery through an incision in the neck. It is a traditional and effective treatment option for severe stenosis.
- Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS): This minimally invasive procedure, performed by an interventional radiologist, offers an alternative to surgery. A thin catheter is inserted through the groin or arm and navigated to the narrowed artery using fluoroscopy (real-time X-ray imaging). A balloon is then inflated to widen the artery, followed by placement of a stent (tiny mesh tube) to keep it open. CAS offers faster recovery times and may be suitable for patients who are not ideal candidates for open surgery.
A Closer Look at Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS):
CAS, performed by a skilled interventional radiologist, offers a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery for carotid stenosis. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the procedure:
-
Preparation: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the area where the catheter will be inserted, typically the groin or arm. You may also receive medication to help you relax during the procedure.
-
Catheter Access: A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into the chosen artery and carefully guided using fluoroscopy (live X-ray imaging) to reach the narrowed carotid artery in your neck.
-
Balloon Angioplasty: Once the catheter reaches the blockage, a tiny balloon attached to another catheter is positioned within the narrowed area. The balloon is then inflated, widening the artery and improving blood flow.
-
Stent Placement: To prevent the artery from narrowing again after balloon angioplasty, a stent (a small, expandable mesh tube) is placed within the opened area. The stent acts like a scaffold, holding the artery open and ensuring a smooth passage for blood flow.
-
Closure and Recovery: Once the stent is positioned, the balloon and catheters are removed. The access point in the groin or arm is typically closed with a closure device or light pressure, minimizing the need for stitches.
Benefits of CAS:
Compared to traditional carotid endarterectomy surgery, CAS offers several advantages:
- Minimally invasive: This reduces the risk of complications associated with open surgery.
- Faster recovery time: Most patients can go home the next day after CAS, while surgical recovery often takes longer.
- Local anesthesia: CAS usually requires only local anesthesia, minimizing the risks associated with general anesthesia used in surgery.
- Suitable for some high-risk patients: CAS may be a good option for patients who are not considered ideal candidates for open surgery due to underlying health conditions.
Important Considerations for CAS:
While CAS offers a promising minimally invasive approach, it’s not suitable for everyone. Here are some things to consider:
- Severity of stenosis: The severity of the blockage plays a role in determining the best course of treatment. CAS may not be suitable for very severe blockages.
- Patient anatomy: The specific anatomy of your carotid arteries can influence whether CAS is the best option.
- Individual risk factors: Your overall health and risk factors for stroke will be considered when deciding if CAS is the right approach for you.
Living with Carotid Stenosis: Long-Term Management
Following successful treatment for carotid stenosis, whether through lifestyle modifications, CAS, or CEA, long-term management is crucial to prevent future blockages and stroke risk. This includes:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Continuing a healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation are essential for reducing your risk factors.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications to manage cholesterol, blood pressure, and other underlying health conditions.
- Regular check-ups: Scheduled follow-up appointments with your doctor are important to monitor your condition and ensure the long-term success of the treatment.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Brain Health
Carotid stenosis can be a silent threat, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, you can significantly reduce your risk of stroke and safeguard your brain health. By understanding the condition, its symptoms, and the available treatment options, you can take an active role in managing your health. Remember, consulting a healthcare professional for personalized diagnosis and treatment planning is vital. Don’t hesitate to discuss your concerns and explore the best approach for managing carotid stenosis and protecting your long-term health.